


Improving outcomes for people with Cardiovascular Disease
A cost-effective digital care model that gets results
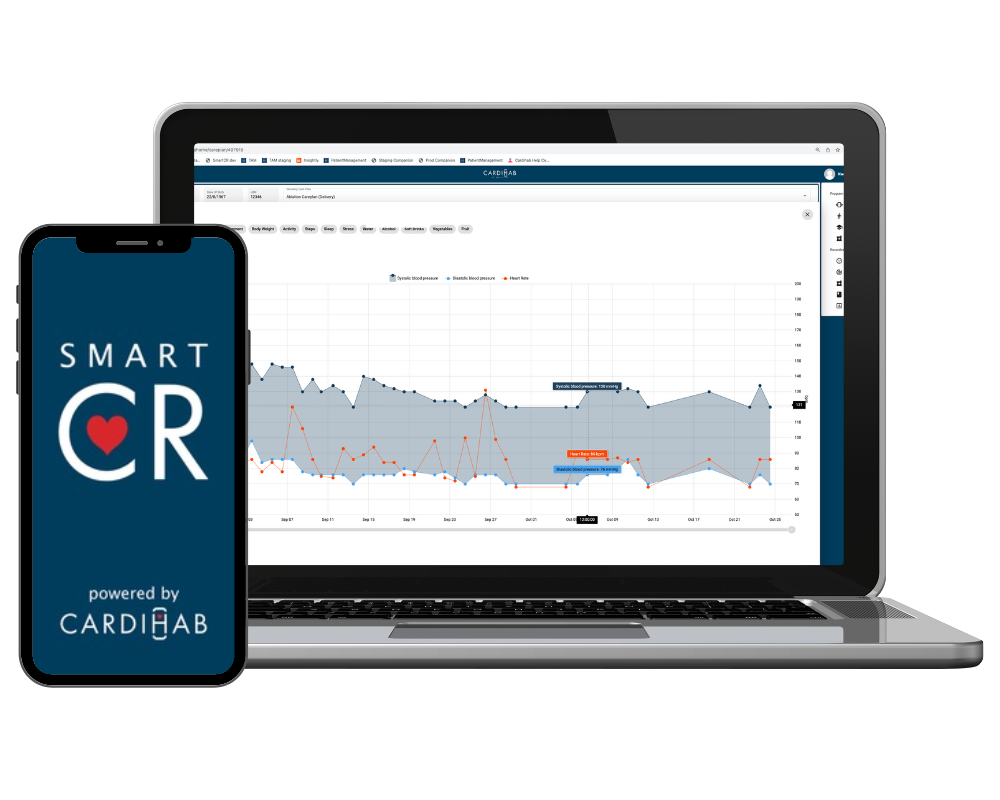
Pioneering virtual cardiac care
Australia's first clinically proven Digital Therapeutic platform for Cardiac Rehabilitation
Evidence-Based Care
A randomised controlled trial demonstrated the Cardihab digital solution offers advantages over the traditional, in-clinic model.

Proven to improve access and outcomes2
80%
UPTAKE
Traditional: 63%
94%
ADHERENCE
Traditional: 68%
80%
COMPLETION
Traditional: 47%
REDUCED ANXIETY
and psychological distress
SIGNIFICANT IMPROVEMENTS
to Health Related Quality of Life

Providing personalised, flexible options for the 80% that miss out on cardiac rehab*
Our platform bridges the gap in cardiac rehabilitation, making it more convenient and accessible to those who need it.
*Randal. Et al. Home-Based Cardiac Rehabilitation: A scientific statement from the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation, the American Heart Association, and the American College of Cardiology. 2019.
Our digital solutions deliver
Transforming cardiac rehabilitation through innovative digital technology

Making cardiac rehabilitation accessible to everyone, anywhere.

Helping patients stay healthy and out of the hospital.

Cost-effective solutions for healthcare providers.

Real-time analytics for better patient outcomes.

Better quality of life for cardiac patients.
How it works
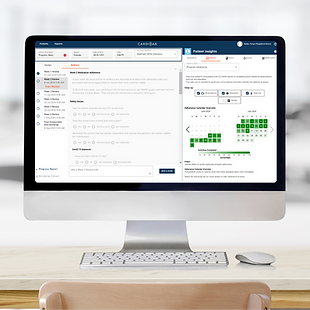
Clinician Portal
Our clinician portal enables the healthcare professional to personalise the virtual care plans that are aligned with clinical guidelines, so they can securely monitor their participants progress.

Designed with participants, for participants
User friendly apps for smart phones, tablets or computers via a web browser are available when and where participants want to complete their program.

Specialised support
Our specialised clinical implementation team provide training and ongoing support to enable successful implementation of a digital health program.
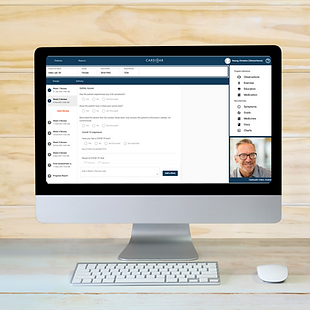
Simple video calling
Easy-to-use integrated telehealth and video calling for communication between participants and their clinician.
Get Started with Cardihab
Transform your cardiac rehabilitation or disease prevention programs with our innovative digital solutions

Why Choose Cardihab?
- Clinically proven results
- Easy to implement
- Comprehensive support
Contact us for a demonstration
REFERENCES:
- Rivers JT, Smith C, Smith I, Cameron J. The impact of a mobile app on participation in cardiac rehabilitation and understanding barriers to success: comparative cohort study. JMIR Cardio. 2022;6(1):e24174. doi:10.2196/24174
- Varnfield M, Karunanithi M, Lee CK, et al. Smartphone-based home care model improved use of cardiac rehabilitation in post myocardial infarction patients: results from a randomised controlled trial. Heart. 2014;100(22):1770-1779. doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2014-305783
- Kraal JJ, Van den Akker-Van Marle ME, Abu-Hanna A, et al. Clinical and cost-effectiveness of home-based cardiac rehabilitation compared to conventional, centre-based cardiac rehabilitation: Results of the FIT@Home study. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2017;24(12):1260-1273. doi:10.1177/2047487317710803
- Braver J, Marwick TH, Oldenburg B, Issaka A, Carrington MJ. Digital Health Programs to Reduce Readmissions in Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JACC Adv. 2023 Sep 7;2(8):100591. doi: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2023.100591. PMID: 38938339; PMCID: PMC11198697.








